Getting Started
What is a WebView? Differences between a WebView and a Browser
Before we get started, we should talk about the differences between a WebView and a Browser.
A WebView is a tool that allows you to display web content within a mobile or desktop application. However, it is not a full browser. This means that many advanced browser features (such as managing multiple tabs, extensions, advanced security features, developer tools, etc.) may not be available or will need to be manually implemented.
If you wish to create an app that behaves like a browser, it is possible to do so using WebViews, but keep in mind that there will be limitations depending on the platform (Android, iOS, Windows, etc.). Each operating system has rules and restrictions that might affect your implementation. For example, advanced features such as file system access or handling custom HTTPS certificates may require additional configurations.
A WebView is primarily designed to embed web content into native apps, rather than providing a complete browsing experience like a full browser. If your project requires browser-like functionality, it's important to be aware of these differences and the potential challenges.
Here you can find a Browser example implemented using this plugin: https://github.com/pichillilorenzo/flutter_browser_app
Let's get started now!
Installation
Add flutter_inappwebview as a dependency in your pubspec.yaml file.
If you're running an application and need to access the binary messenger before runApp() has been called (for example, during plugin initialization), then you need to explicitly call the WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized() first.
An example:
void main() {
// it should be the first line in main method
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
// rest of your app code
runApp(MyApp());
}
Requirements
- Dart sdk: "^3.5.0"
- Flutter: ">=3.24.0"
- Android:
minSdkVersion >= 19,compileSdk >= 34, AGP version>= 7.3.0(use Android Studio - Android Gradle plugin Upgrade Assistant for help), support forandroidx(see AndroidX Migration to migrate an existing app) - iOS 12.0+:
--ios-language swift, Xcode version>= 15.0 - MacOS 10.14+: Xcode version
>= 15.0 - Windows: NuGet CLI available on your PATH environment variable
Native WebView implementation
These are the native WebView classes used by the plugin to implement its features:
- Android: android.webkit.WebView
- iOS: WebKit/WKWebView
- macOS: WebKit/WKWebView
- Windows: Microsoft.Web.WebView2
- Web: HTMLIFrameElement
Since each platform has its own native implementation, keep in mind that in some cases they may behave differently.
Setup Android
If you are starting a new fresh app, you need to create the Flutter App with flutter create --androidx -i swift to add support for androidx, otherwise it won't work (see AndroidX Migration to migrate an existing app).
During the build, if Android fails with Error: uses-sdk:minSdkVersion 16 cannot be smaller than version 19 declared in library, it means that you need to update the minSdkVersion of your android/app/build.gradle file to at least 19.
Also, you need to add <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> in the android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml file in order to give minimum permission to perform network operations in your application.
If you flutter created your project prior to version 1.12, you need to make sure to update your project in order to use the new Java Embedding API! Take a look at the official Flutter wiki: Upgrading pre 1.12 Android projects. Also, you can refer to the #343 issue.
Remember to add <meta-data> tag inside the <application> tag of your android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml:
<meta-data
android:name="flutterEmbedding"
android:value="2" />
as mentioned in the 6th step of Full-Flutter app migration guide. Without this, the plugin will NOT work!!!
Also, note that to use the InAppWebView widget on Android, it requires Android API 20+ (see AndroidView) or Android API 19+ if you enable the useHybridComposition Android-specific option.
Support HTTP (non-HTTPS) request
Starting with Android 9 (API level 28), cleartext support is disabled by default:
- Check the official Network security configuration - "Opt out of cleartext traffic" section.
- Also, check this StackOverflow issue answer: Cleartext HTTP traffic not permitted.
ChromeSafariBrowser on Android 11+
If you want to use the ChromeSafariBrowser class on Android 11+ you need to specify your app querying for android.support.customtabs.action.CustomTabsService in your AndroidManifest.xml (you can read more about it here: https://developers.google.com/web/android/custom-tabs/best-practices#applications_targeting_android_11_api_level_30_or_above).
Enable Material Components for Android
To use Material Components when the user interacts with input elements in the WebView, follow the steps described in the Enabling Material Components instructions.
Setup iOS
If you are starting a new fresh app, you need to create the Flutter App with flutter create --androidx -i swift (see flutter/flutter#13422 (comment)), otherwise, you will get this message:
=== BUILD TARGET flutter_inappwebview OF PROJECT Pods WITH CONFIGURATION Debug ===
The "Swift Language Version" (SWIFT_VERSION) build setting must be set to a supported value for targets which use Swift. Supported values are: 3.0, 4.0, 4.2, 5.0. This setting can be set in the build settings editor.
If you still have this problem, try to edit iOS Podfile like this (see #15):
target 'Runner' do
use_frameworks! # required by simple_permission
...
end
post_install do |installer|
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings['SWIFT_VERSION'] = '5.0' # required by simple_permission
config.build_settings['ENABLE_BITCODE'] = 'NO'
end
end
end
Instead, if you have already a non-swift project, you can check this issue to solve the problem: Friction adding swift plugin to objective-c project.
Support HTTP (non-HTTPS) request
You need to disable Apple Transport Security (ATS) feature. There're two options:
- Disable ATS for a specific domain only (Official wiki): (add following codes to your
Info.plistfile)
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSExceptionDomains</key>
<dict>
<key>www.yourserver.com</key>
<dict>
<!-- add this key to enable subdomains such as sub.yourserver.com -->
<key>NSIncludesSubdomains</key>
<true/>
<!-- add this key to allow standard HTTP requests, thus negating the ATS -->
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionAllowsInsecureHTTPLoads</key>
<true/>
<!-- add this key to specify the minimum TLS version to accept -->
<key>NSTemporaryExceptionMinimumTLSVersion</key>
<string>TLSv1.1</string>
</dict>
</dict>
</dict>
- Completely disable ATS (Official wiki): (add following codes to your
Info.plistfile)
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key><true/>
</dict>
Other useful Info.plist properties are:
NSAllowsLocalNetworking: A Boolean value indicating whether to allow loading of local resources (Official wiki);NSAllowsArbitraryLoadsInWebContent: A Boolean value indicating whether all App Transport Security restrictions are disabled for requests made from web views (Official wiki).
Setup MacOS
To be able to make HTTP requests, you need to configure the macOS App Sandbox by enabling the Outgoing Connections (Client) option in your MacOS XCode Project, under Runner > Signing & Capabilities.
Here is an example of configuration:
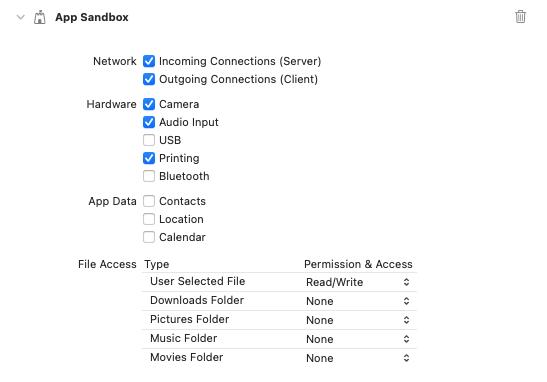
For more details, check the Apple Official Guide.
Setup Windows
To be able to build on Windows, you must have the nuget CLI tool available on your Windows environment.
Follow the instructions here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/nuget/install-nuget-client-tools?tabs=windows#nugetexe-cli
Add the folder location for the nuget.exe file to your Windows PATH environment variable.
Setup Web
To make it work properly on the Web platform, you need to add the web_support.js file inside the <head> of your web/index.html file:
<head>
<!-- ... -->
<script type="application/javascript" src="/assets/packages/flutter_inappwebview_web/assets/web/web_support.js" defer></script>
<!-- ... -->
</head>
When overlaying Flutter widgets on top of HtmlElementView widgets that respond to mouse gestures (handle clicks, for example), the clicks will be consumed by the HtmlElementView, and not relayed to Flutter.
The result is that Flutter widget's onTap (and other) handlers won't fire as expected, but they'll affect the underlying webview.
This is an issue of Flutter itself and not of this plugin.
To overcome this problem, you should use the official pointer_interceptor Flutter plugin. Check the pointer_interceptor plugin docs to understand how to use it.
Load files inside the assets folder
To be able to make visible your local asset files (images, javascript, css, etc.) to Flutter, you need to add them in the assets section of the pubspec.yaml file, otherwise they cannot be found.
Read the official Flutter documentation Adding assets and images for more details.
Example of a pubspec.yaml file:
...
# The following section is specific to Flutter.
flutter:
# The following line ensures that the Material Icons font is
# included with your application, so that you can use the icons in
# the material Icons class.
uses-material-design: true
assets:
- assets/index.html
- assets/css/
- assets/images/
...
Enable camera for HTML inputs
In order to be able to use camera, for example, for taking images through <input type="file" accept="image/*" capture> HTML tag, you need to ask camera permission. If you need to capture video and audio, you need to ask also microphone permission.
To ask permissions, for example, you can use the permission_handler plugin!
Code example:
import 'package:permission_handler/permission_handler.dart';
Future main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
await Permission.camera.request();
await Permission.microphone.request(); // if you need microphone permission
runApp(MyApp());
}
Configure Android
On Android, you need to add these permissions in your AndroidManifest.xml file to be able to use camera for taking images and videos:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIDEO_CAPTURE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.AUDIO_CAPTURE" />
Also, you need to add the following code inside the <application> tag of your AndroidManifest.xml file:
<provider
android:name="com.pichillilorenzo.flutter_inappwebview_android.InAppWebViewFileProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.flutter_inappwebview_android.fileprovider"
android:exported="false"
android:grantUriPermissions="true">
<meta-data
android:name="android.support.FILE_PROVIDER_PATHS"
android:resource="@xml/provider_paths" />
</provider>
Configure iOS
On iOS, you need to add the following properties in your Info.plist file to be able to use camera for taking images and videos:
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Flutter requires access to microphone.</string>
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Flutter requires access to camera.</string>
If you open this file In Xcode, then the NSMicrophoneUsageDescription property is represented by Privacy - Microphone Usage Description and NSCameraUsageDescription is represented by Privacy - Camera Usage Description.
Did you find it useful? Consider making a donation to support this project and leave a star on GitHub 